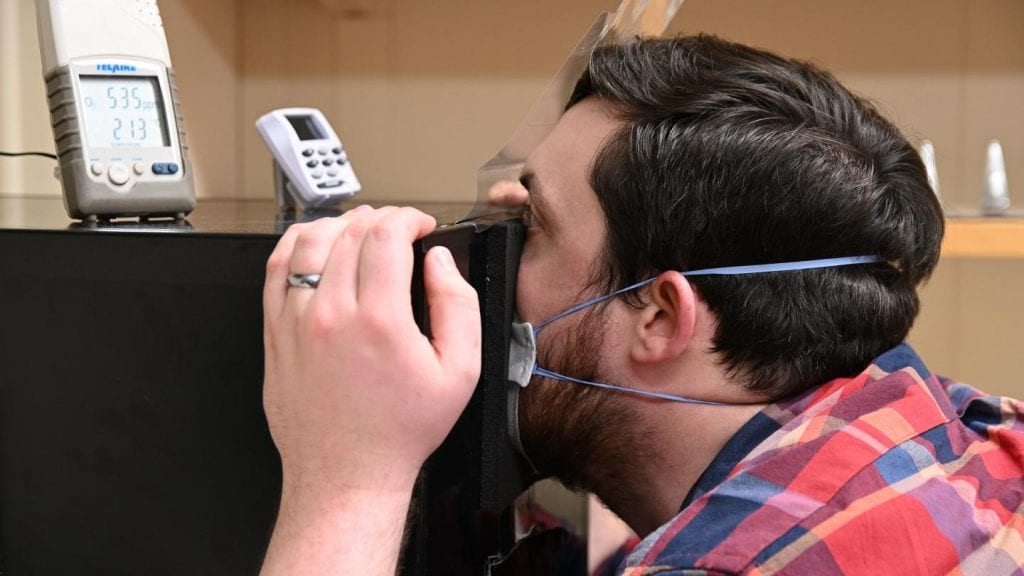
Masks help protect the people wearing them from getting or spreading SARS-CoV-2, the virus that causes COVID-19, but now researchers from the National Institutes of Health have added evidence for yet another potential benefit for wearers: The humidity created inside the mask may help combat respiratory diseases such as COVID-19.
The study, led by researchers in the NIH’s National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK), found that face masks substantially increase the humidity in the air that the mask-wearer breathes in. This higher level of humidity in inhaled air, the researchers suggest, could help explain why wearing masks has been linked to lower disease severity in people infected with SARS-CoV-2, because hydration of the respiratory tract is known to benefit the immune system. The study published in the Biophysical Journal.
Continue reading “Researchers propose that humidity from masks may lessen severity of COVID-19”